# Vue2.x和Vue3.x渲染器的diff算法
# dom-diff概述
比较只会在同层级进行, 不会跨层级比较
# Vue2.x diff算法
# 1.vue2.x dom-diff算法核心源码
function updateChildren(parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
var oldStartIdx = 0;//旧节点开始index
var newStartIdx = 0;//新节点开始index
var oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1;//旧节点结束index
var oldStartVnode = oldCh[0];//旧节点开始节点VNode
var oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx];//旧节点结束节点
var newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1;//新节点结束index
var newStartVnode = newCh[0];//新节点开始节点VNode
var newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx];//新节点结束虚拟节点VNode
//核心dom-diff 算法
//新旧节点两个指针,做比较
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
//1.旧开始节点 === undefined
if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
//2.旧结束节点 === undefined
} else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
//3.旧开始节点 === 新开始节点
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx);
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
//4.旧结束节点 === 新结束节点
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
//5.旧开始节点 === 新结束节点
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx);
//操作真实dom:将老开始节点放置在老结束节点的后面,占了老节点的结束节点位置
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm));
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
//6.旧结束节点 === 新开始节点
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx);
//操作真实dom:将结束节点放置在开始节点前面,因为这里指针有移动,作用就是原本的位置
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
//7.都不是
} else {
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) {
//返回老节点的key-index的映射表
oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}
idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key)
? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
: findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
//index不存在,就是新增的元素
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) {
//实操dom:新增VNode,并且添加到dom中
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx);
} else {
//不是新增元素,则移动
//需要移动的VNode
vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld];
//比较需要移动的VNode和现在新开始节点是否相同
if (sameVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) {
//打补丁,以及遍历子节点
patchVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx);
//将老虚拟dom此处的VNode删除
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined;
//实操dom
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm, oldStartVnode.elm);
} else {
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx);
}
}
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}
}
/*
1.如果开始下标大于结束下标,说明遍历老节点遍历结束
2.老节点遍历完毕,新节点的下标+1的值,添加进去
3.如果新节点遍历完了,就删除老节点中开始到结束下标的值
*/
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm;
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
//老的没有遍历完,新的遍历完了
//删除老的的节点,从start开始,end结束,包括end
//这里原先移动了节点,用undefined占位,直接删除不影响任何节点
removeVnodes(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
# 2. 整体逻辑图
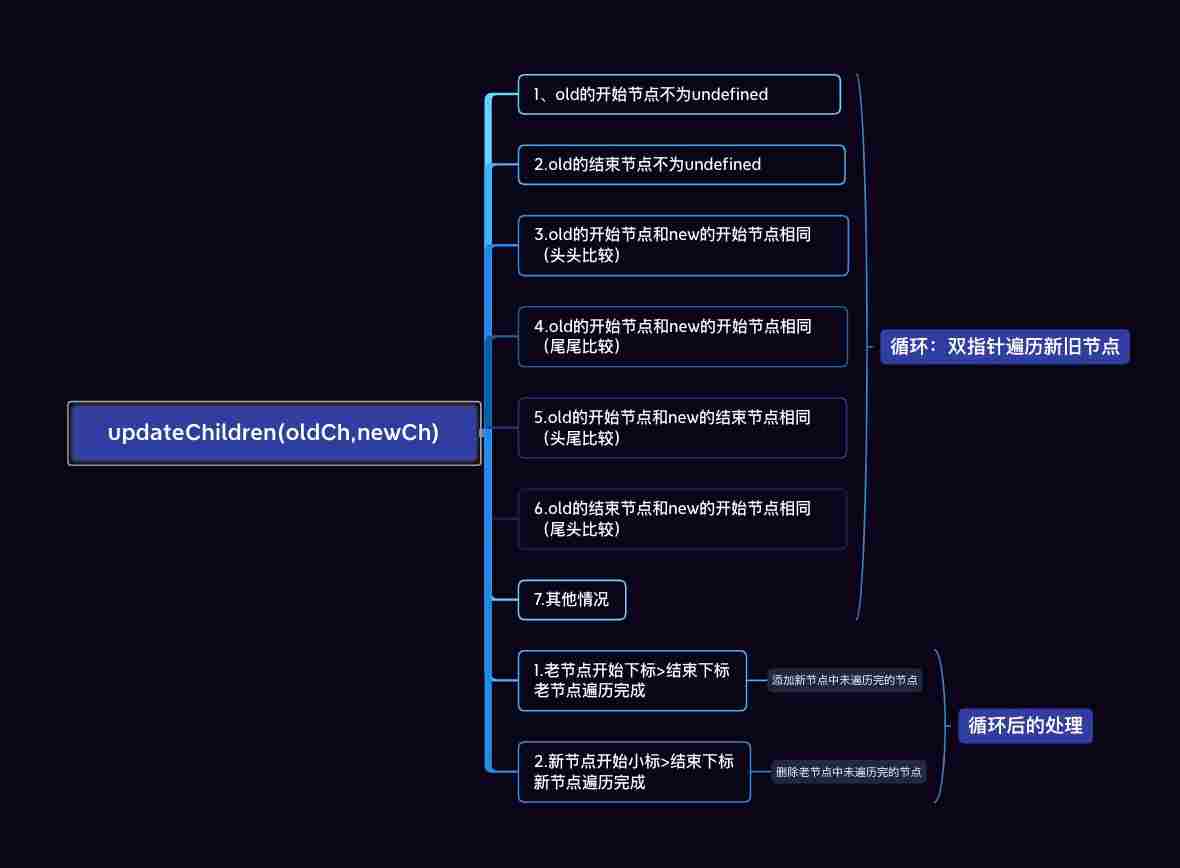
# 3.案例分析
realDom
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
//old VNode
l r
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
//new VNode
a b
[1, 9, 11, 7, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2, 10]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
** 注意这里比较的都是虚拟dom节点:真实dom的移动不影响虚拟dom节点值,可参照动图一起看
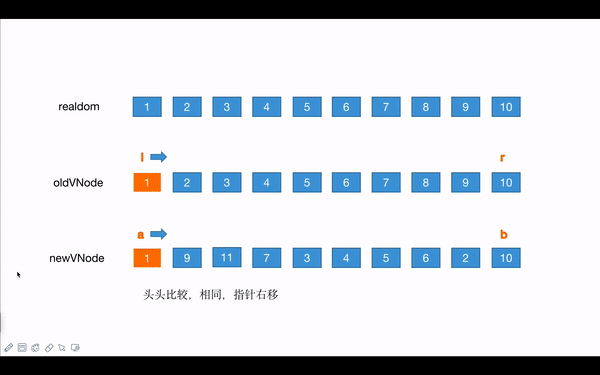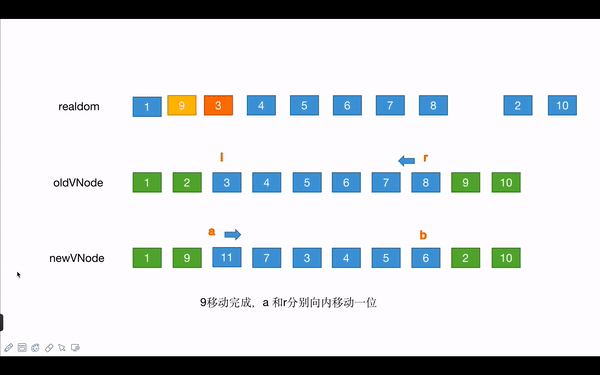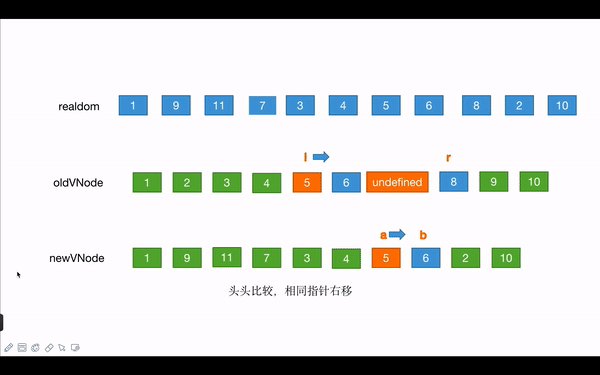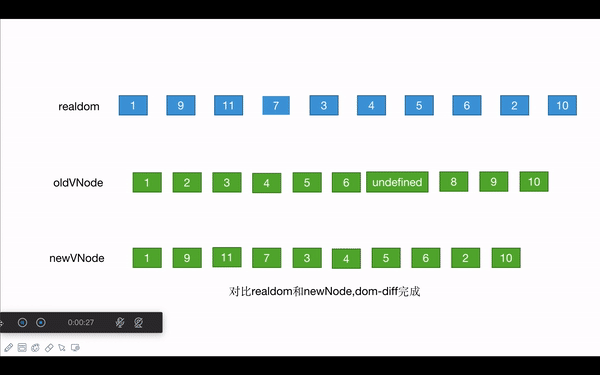
- 新旧头比较,直到第一个不相同的节点:
l和a都向右移动一位 ,都为1 - 新旧尾比较,直到第一个不相同的节点:
r和b都向左移动一位,都为9 - 旧头和新尾比较,相同的话,开始移动真实的dom:
- **旧头真实dom移动到旧尾紧跟其后的兄弟节点的前面:**真实dom中,2移动到10前面,原生节点插入方式实现
- 指针移动:旧开始指针向右移动一位,新结束指针向左移动一位 此时,
l变成了2,b变成了8 - 此时的真实dom为:
1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 10
- 旧尾和新头比较,相同的话,移动真实dom:
- 旧尾真实dom移动到旧头节点的el的前面:真实dom中,9移动到3的前面
- 旧尾指针向左移动一位,新头指针向右移动一位,此时,
a变成了2,r变成了8 - 此时的真实dom为:
1 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 10
- 此时四个指针已经不满足上面四种情况了,就需要进一步处理
- 首先遍历剩余老节点,返回一个
key:oldIndex映射表 - 新节点的开始节点在这个映射表中能找到对应的oldIndex,说明在老节点中存在这个节点,只需要移动即可
- 如果不存在,则需要新建节点,并且插入到指定的位置
- 首先遍历剩余老节点,返回一个
接着分析案例:
- 剩下的老节点为:
[3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]映射表为{3: 2, 4: 3, 5: 4, 6: 5, 7: 6, 8: 7}剩下的新节点的为[11, 7, 3, 4, 5, 6]此时11在映射表中,没有查询到,说明是新增的节点 - 新增节点
11,通过createElm函数创建真实dom,并且插入到旧开始节点el指向的真实dom前面。此时旧开始节点是3,真实dom中11插入到3的前面。 - 新开始指针向右移动一位,
a变成3 - 此时的真实dom :
1 9 11 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 10
- 接着分析:此时老节点剩余
3,4,5,6,7,8新节点剩余7,3,4,5,6此时又符合情况五。- 先找到
7在老节点的index,根据映射表,oldIndex为6说明在老节点中存在,只需要移动 - 将
7真实dom中的el移动到老开始节点的el前面,也就是真实dom中3的前面 - 将老节点中
oldIndex这个节点设置为undefined,后面会讲作用 - 新开始指针向右移动一位,
a变成了4 - 此时的真实dom :
1 9 11 7 3 4 5 6 8 2 10
- 先找到
- 此时老节点剩余
3,4,5,6,7,8新节点剩余3,4,5,6此时符合情况一,头头比较,遍历完新节点,循环结束 - 接下来是循环结束后的处理,也就是查看新旧节点是否都完全遍历
- 此时旧节点还未完全遍历,剩下
7,8,说明这是需要删除的节点 - 因为
7是被移动的节点,在移动之后,将其虚拟节点数组中的位置设置成了undefined避免了后续将其删除 - 根据
8虚拟节点的elm属性,将其真实dom中的el删除
- 此时旧节点还未完全遍历,剩下
总结:整个Vue2.x的dom-diff过程就完成了,需要注意的几点是,
- 双指针遍历的是,新旧的虚拟节点数组,不是真实dom
- 老节点都有elm属性,指向真实的节点,节点的插入和删除都是依靠这个属性
- Vue2.x尽可能在复用原本的dom
- 尽量使用key,在不使用key时,所有的节点对比都是相同的,对比情况都是走的头头比较,节点都是直接对比然后进行修改处理,比复用移动老节点效率低。
# Vue3.x diff算法
# 1. Vue3.x dom-diff 核心源码
const patchKeyedChildren = (c1, c2, container, parentAnchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized) => {
let i = 0;
const l2 = c2.length;
let e1 = c1.length - 1; // prev ending index
let e2 = l2 - 1; // next ending index
// 1. sync from start
// (a b) c
// (a b) d e
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[i];
const n2 = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i])
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]));
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(n1, n2, container, parentAnchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized);
}
else {
break;
}
i++;
}
// 2. sync from end
// a (b c)
// d e (b c)
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
//获取末尾的值
const n1 = c1[e1];
const n2 = (c2[e2] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[e2])
: normalizeVNode(c2[e2]));
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(n1, n2, container, parentAnchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized);
}
else {
break;
}
e1--;
e2--;
}
// 3. common sequence + mount
// (a b)
// (a b) c
// i = 2, e1 = 1, e2 = 2
// (a b)
// c (a b)
// i = 0, e1 = -1, e2 = 0
//旧节点遍历完全,patch c2剩下的节点
if (i > e1) {
if (i <= e2) {
const nextPos = e2 + 1;
const anchor = nextPos < l2 ? c2[nextPos].el : parentAnchor;
while (i <= e2) {
patch(null, (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i])
: normalizeVNode(c2[i])), container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG);
i++;
}
}
}
// 4. common sequence + unmount
// (a b) c
// (a b)
// i = 2, e1 = 2, e2 = 1
// a (b c)
// (b c)
// i = 0, e1 = 0, e2 = -1
//新节点遍历完全,卸载老节点上的多余节点
else if (i > e2) {
while (i <= e1) {
unmount(c1[i], parentComponent, parentSuspense, true);
i++;
}
}
// 5. unknown sequence
// [i ... e1 + 1]: a b [c d e] f g
// [i ... e2 + 1]: a b [e d c h] f g
// i = 2, e1 = 4, e2 = 5
else {
const s1 = i; // prev starting index
const s2 = i; // next starting index
// 5.1 build key:index map for newChildren
const keyToNewIndexMap = new Map();
for (i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {
const nextChild = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i])
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]));
if (nextChild.key != null) {
if ((process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') && keyToNewIndexMap.has(nextChild.key)) {
warn(`Duplicate keys found during update:`, JSON.stringify(nextChild.key), `Make sure keys are unique.`);
}
keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i);
}
}
// 5.2 loop through old children left to be patched and try to patch
// matching nodes & remove nodes that are no longer present
let j;
let patched = 0;
const toBePatched = e2 - s2 + 1;
let moved = false;
let maxNewIndexSoFar = 0; // used to track whether any node has moved
// works as Map<newIndex, oldIndex>
// Note that oldIndex is offset by +1
// and oldIndex = 0 is a special value indicating the new node has
// no corresponding old node.
// used for determining longest stable subsequence
const newIndexToOldIndexMap = new Array(toBePatched);
for (i = 0; i < toBePatched; i++)
newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] = 0;
//先遍历老节点
for (i = s1; i <= e1; i++) {
//老的子节点
const prevChild = c1[i];
//挂载完成,删除当前老的子节点
if (patched >= toBePatched) {
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true);
continue;
}
//获取newIndex
let newIndex;
if (prevChild.key != null) {
newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key);
}
else {
// key-less node, try to locate a key-less node of the same type
//没有key的节点,尝试去定位一个与其相同类型的节点
//遍历新节点
for (j = s2; j <= e2; j++) {
//遍历s2到e2,找出和prevChild类型相同的节点,并将j赋值给newIndex
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[j - s2] === 0 && isSameVNodeType(prevChild, c2[j])) {
newIndex = j;
break;
}
}
}
//newIndex不存在,则卸载节点
if (newIndex === undefined) {
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true);
}
else {
//新节点存在
newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex - s2] = i + 1; //i为s1
if (newIndex >= maxNewIndexSoFar) {
maxNewIndexSoFar = newIndex;
}
else {
moved = true;
}
patch(prevChild, c2[newIndex], container, null, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized);
patched++;
}
}
// 5.3 move and mount
// generate longest stable subsequence only when nodes have moved
//新节点数组中最大升序子集,返回的是index集合
const increasingNewIndexSequence = moved
? getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap)
: EMPTY_ARR;
j = increasingNewIndexSequence.length - 1;
//向后循环,以便我们可以使用最后一个补丁节点作为锚
for (i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
//新的子节点下标和新的子节点
const nextIndex = s2 + i;
const nextChild = c2[nextIndex];
//nextIndex后面一个节点为锚点
const anchor = nextIndex + 1 < l2 ? c2[nextIndex + 1].el : parentAnchor;
//为0则是新增
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] === 0) {
// 挂载新节点
patch(null, nextChild, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG);
}
else if (moved) {
//在没有稳定升序子集的的情况,或者现在的节点不在稳定升序子集里面,则移动
//i是遍历需要移动节点集合的指针,从后往前
//j是从后往前遍历increasingNewIndexSequence的指针
// j<0则最长升序子集遍历完成 i!== 子序列中的值,说明需要移动
if (j < 0 || i !== increasingNewIndexSequence[j]) {
move(nextChild, container, anchor, 2 /* REORDER */);
}
else {
j--;
}
}
}
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
# 2. 整体逻辑图
 和vue2.x对比,Vue3.0没有采用双指针遍历的方式,而是单指针循环,先遍历头部节点,直到第一个不同节点;然后再尾部遍历,直到第一个不同的节点。然后做新旧节点是否遍历完成的判断,如果遍历完成则进行挂载或删除。以上情况都不是,则进行核心逻辑对比。Vue3.x中取消了头尾/尾头的比较,只要头尾遇到不同的节点,那么其中的节点都进入未知序列核心逻辑的比较。先看一下核心对比的逻辑图
此处的 unknown sequence 就是上例中的除去头尾相同项的中间项
和vue2.x对比,Vue3.0没有采用双指针遍历的方式,而是单指针循环,先遍历头部节点,直到第一个不同节点;然后再尾部遍历,直到第一个不同的节点。然后做新旧节点是否遍历完成的判断,如果遍历完成则进行挂载或删除。以上情况都不是,则进行核心逻辑对比。Vue3.x中取消了头尾/尾头的比较,只要头尾遇到不同的节点,那么其中的节点都进入未知序列核心逻辑的比较。先看一下核心对比的逻辑图
此处的 unknown sequence 就是上例中的除去头尾相同项的中间项

# 3. 案例分析
还是上面的案例
realDom
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
//old VNode
s1 e1
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
//new VNode
s2 e2
[1, 9, 11, 7, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2, 10]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
头尾比较后,主要是中间项的比较。
oldch:: [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
newch:[9, 11, 7, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2]
结合动图
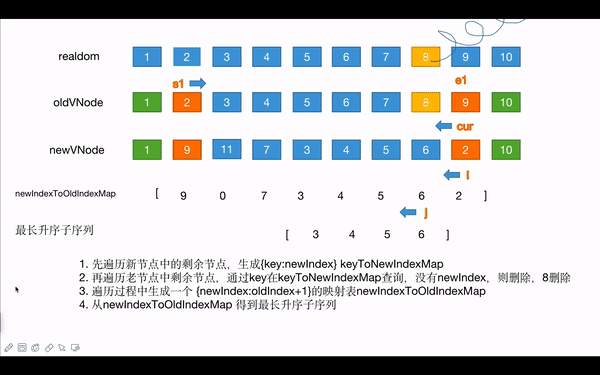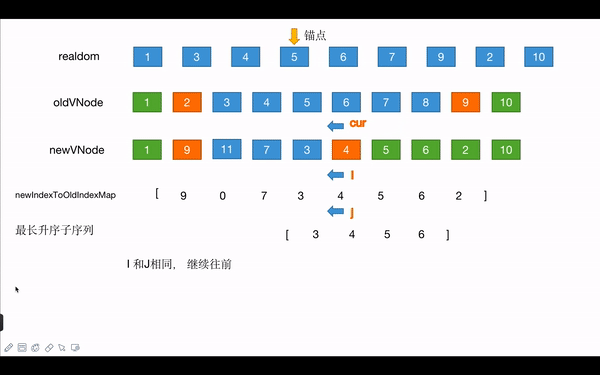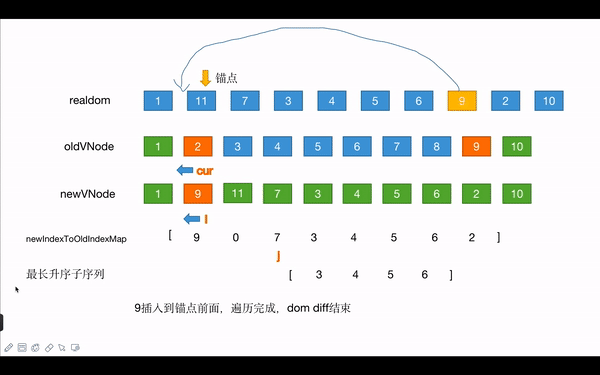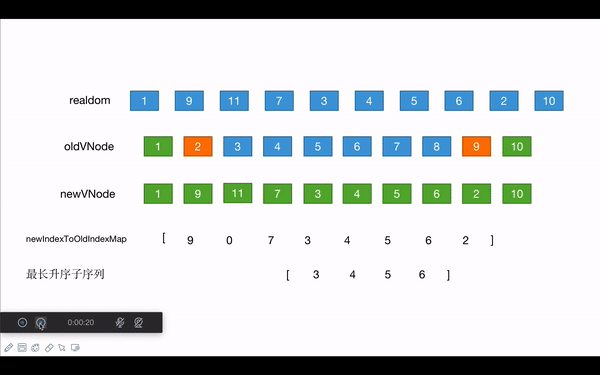
- 首先遍历新的子节点,生成一个新节点自身key和index的映射表:
keyToNewIndexMap
0: {9 => 1}
1: {11 => 2}
2: {7 => 3}
3: {3 => 4}
4: {4 => 5}
5: {5 => 6}
6: {6 => 7}
7: {2 => 8}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 遍历旧节点
- 通过旧节点的key,在中
keyToNewIndexMap查询在新节点index - 如果newIndex没有,则删除节点
- 如果有,就生成一个 {newIndex : oldIndex+1}映射表 :
newIndexToOldIndexMap
- 通过旧节点的key,在中
[9,0,7,3,4,5,6,2]
1
- 通过
newIndexToOldIndexMap获取最长升序子序列的index集合,increasingNewIndexSequence
[3,4,5,6]
1
newch :
[9, 11, 7, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2]newIndexToOldIndexMap:
[9, 0, 7, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2]increasingNewIndexSequence:[3, 4, 5, 6]
- 需要比较的项的数量为8,用toBePatched表示,以数组项指针的形式从后往前循环,同时遍历newch和newIndexToOldIndexMap
- 同时最长升序子序列也从后往前遍历,将其遍历的值和上面遍历的数组指针比较
- newIndexToOldIndexMap指针在increasingNewIndexSequence项中没有的时候,对应的newch中的节点就需要移动;存在的话,则不需移动
- newIndexToOldIndexMap中值为0的时候,对应的newch中的项就为新增节点
- 锚点为,指针移动到newCh节点的后面节点
Vue3.x的dom diff通过和最长升序子序列的的对比,将节点移动操作最小化,大大提升了效率。感兴趣的可以研究下最长升序子序列。
# 4.最长升序子序列算法
function getSequence(arr) {
const p = arr.slice();
const result = [0];
let i, j, u, v, c;
const len = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const arrI = arr[i];
j = result[result.length - 1];
if (arr[j] < arrI) {
p[i] = j;
result.push(i);
continue;
}
u = 0;
v = result.length - 1;
while (u < v) {
c = ((u + v) / 2) | 0;
if (arr[result[c]] < arrI) {
u = c + 1;
}
else {
v = c;
}
}
if (arrI < arr[result[u]]) {
if (u > 0) {
p[i] = result[u - 1];
}
result[u] = i;
}
}
u = result.length;
v = result[u - 1];
while (u-- > 0) {
result[u] = v;
v = p[v];
}
return result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39